Graph product
In mathematics, a graph product is a certain kind of binary operation on graphs. Specifically, it is an operation that takes two graphs G1 and G2 and produces a graph H with the following properties:
- The vertex set of H is the Cartesian product V(G1) × V(G2), where V(G1) and V(G2) are the vertex sets of G1 and G2, respectively.
- Two vertices (u1, u2) and (v1, v2) of H are connected by an edge if and only if the vertices u1, u2, v1, v2 satisfy conditions of a certain type (see below).
The following table shows the most common graph products, with ∼ denoting “is connected by an edge to”:
| Name | Condition for (u1, u2) ∼ (v1, v2). | Dimensions | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cartesian product | ( u1 = v1 and u2 ∼ v2 ) or ( u1 ∼ v1 and u2 = v2 ) |
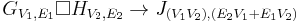 |
|
| Tensor product | u1 ∼ v1 and u2 ∼ v2 | 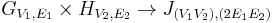 |
|
| Lexicographical product | u1 ∼ v1 or ( u1 = v1 and u2 ∼ v2 ) |
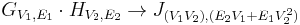 |
|
| Strong product (Normal product, AND product) |
( u1 = v1 and u2 ∼ v2 ) or ( u1 ∼ v1 and u2 = v2 ) or ( u1 ∼ v1 and u2 ∼ v2 ) |
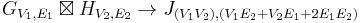 |
|
| Co-normal product (disjunctive product, OR product) |
u1 ∼ v1 or u2 ∼ v2 |
||
| Rooted product | see article | 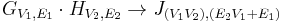 |
In general, a graph product is determined by any condition for (u1, u2) ∼ (v1, v2) that can be expressed in terms of the statements u1 ∼ v1, u2 ∼ v2, u1 = v1, and u2 = v2.
See also
References
- Imrich, Wilfried; Klavžar, Sandi (2000), Product Graphs: Structure and Recognition, Wiley, ISBN 0-471-37039-8.